Flexible nano coatings
Requirements for applications in aqueous environments are met by our high performing and permanent plasma coatings, also regarding the interaction of water with the surface and sub-surface (bioresponse, corrosion, wettability, adhesion, defined degradability etc.). As a research highlight, the orientation of water molecules within hydrophobic-to-hydrophilic layers induces additional interaction forces modulating, for example, protein adsorption.
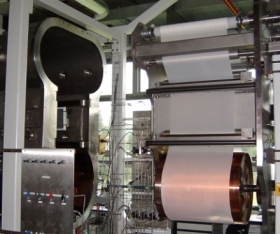
Our knowledge extends to the successful transfer of plasma processes (etching, cleaning, plasma polymerization, sputtering) to industry supported by pilot-plant reactors both for web and fiber coating as well as simulation tools including production cost models.
Activities
- Deposition of plasma coatings with film properties such as hydrophilic/ hydrophobic, antimicrobial, antistatic, conductive,
- Formation of vertical chemical gradient films through variation of plasma conditions during deposition reducing aging effects, improving adhesion, enabling well-controlled drug delivery and affecting protein adsorption.
- Etching processes on polymers exposing embedded structures to the surface or widening pores.
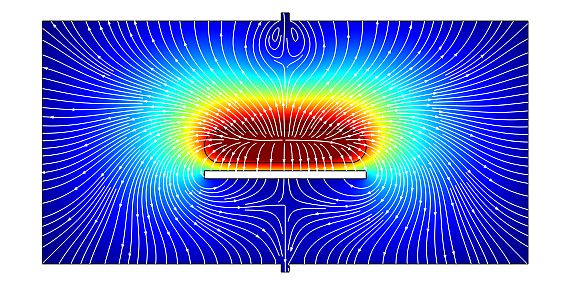
- Development and modification of plasma reactors supporting the optimization of plasma processes, also regarding scalability. By using pilot-plant reactors the conditions for the transfer of plasma processes into industry are examined.
- Simulation of gas flow within plasma reactors and transport of film-forming species to substrate surfaces supporting process optimization and up-scaling.
- Plasma processing of low vapor pressure liquids to obtain thin, freely floating films. Partly crosslinking of liquid molecules among each other and with the plasma-polymerized film leads to functional surfaces showing durable hydrophilic properties.