Chitosan aerogels
Chitosan is derived from chitin, the second most abundant biopolymer on earth and a critical component of the mushroom, insects and crustaceans. Chitosan is produced available in large quantities from waste shrimp and crab shells from food production. Chitosan differs from other polysaccharides because of its amino groups, which open up new applications and provide a highly reactive anchoring point for cross-linking [1]. In our group, we developed a new type of chitosan aerogels through the use of a non-toxic urea cross-linker [2]. These aerogels have excellent thermal and mechanical properties and, unique among biopolymer aerogels, can be produced by ambient pressure drying. In later work, we were able to prepare transparent chitosan aerogels with the same cross-linker [3].
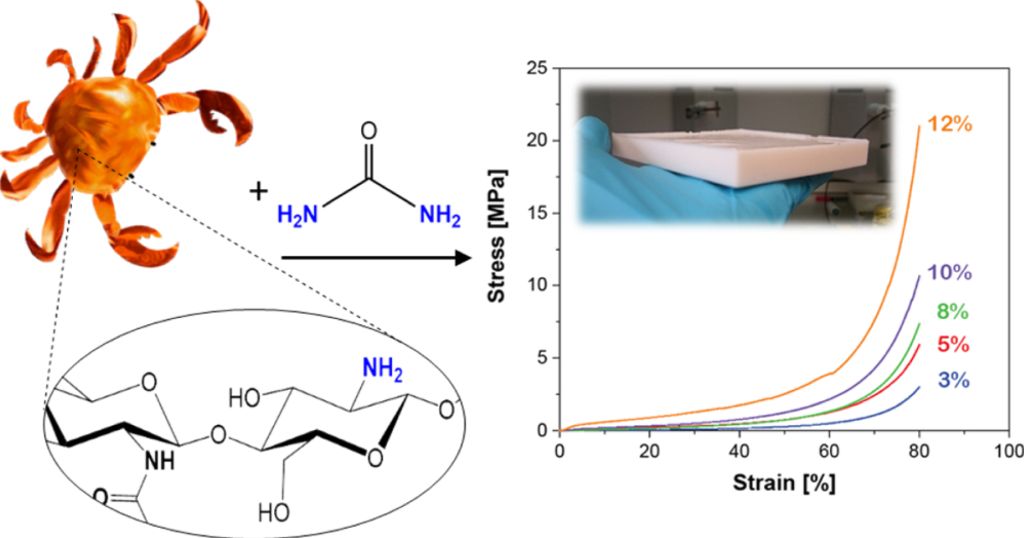
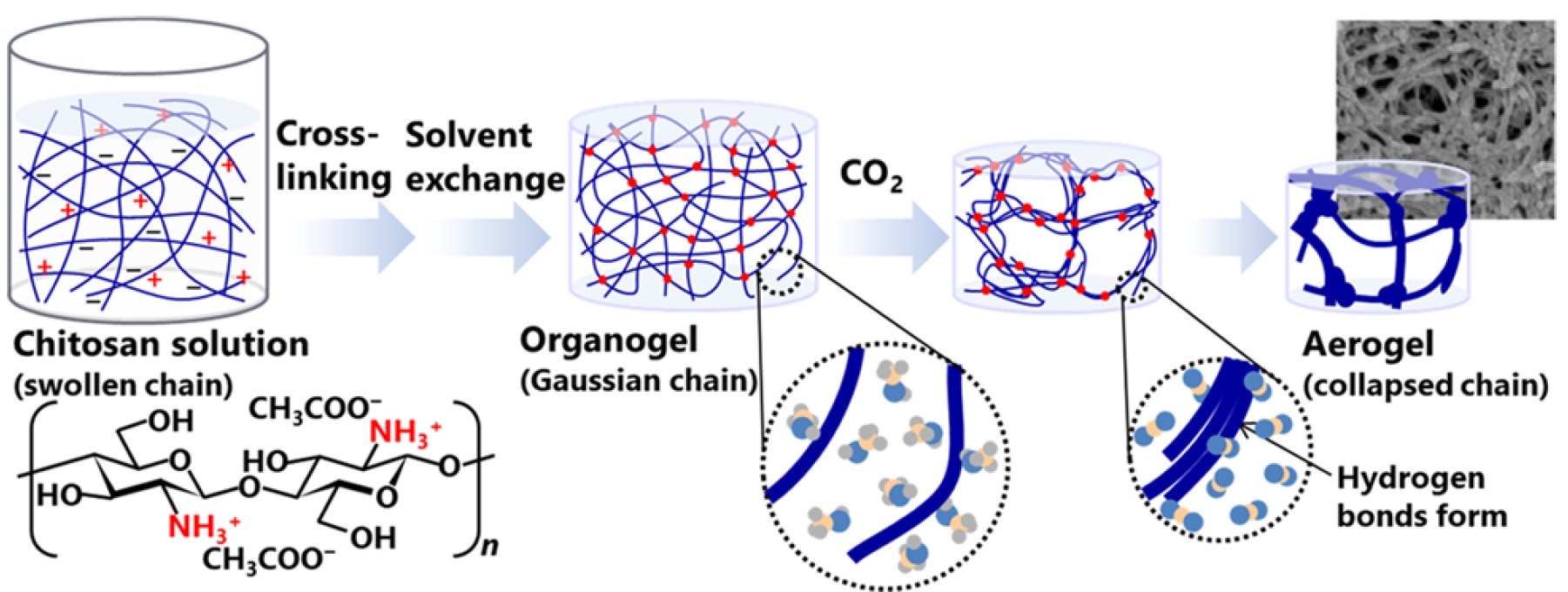
We also use the chitosan system as a model system to investigate the sol-gel and aerogel production process of biopolymer aerogels in detail. In situ SAXS measurements on chitosan solutions, hydrogels, organogels and aerogels indicate that, contrary to the current paradigm, the supercritical CO2 drying process is not always an inert process, but the key structure formation step during chitosan aerogel production [4-5].


-
Share
