Global Atmosphere Watch
Latest news:
QA/SAC-CH recently developed GAW-QC, an interactive dashboard for the quality check of in-situ atmospheric composition measurements made at stations taking part in the Global Atmosphere Watch network. The idea is to facilitate a timely quality control of recent measurements of CO2, CH4, CO, and O3. The tool is able to identify suspicious data and outliers. By using historical data and numerical simulations, the identification is station-specific and accounts for previously observed variability and trends. The dashboard is available here. More information can be found at the QA/SAC-CH webpage (see 'New activity: early detection of data quality issues').
One of the core tasks of the GAW programme is the coordination of the activities and data of currently 32 Global, more than 400 Regional atmospheric monitoring stations, and around 100 Contributing stations operated by contributing networks to produce data that are relevant to air pollution and climate change.
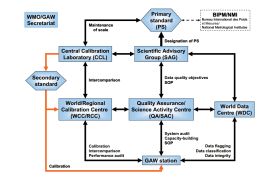
The GAW monitoring programme targets six classes of variables (i.e. ozone, UV radiation, greenhouse gases, aerosols, selected reactive gases and precipitation chemistry). Each of the six variable groups is supported by a Scientific Advisory Group and so called GAW Central Facilities (Quality Assurance/Science Activity Centres, Central Calibration Laboratories, World and Regional Calibration Centres and World Data Centres) responsible for quality control, scientific guidance and technical details of the global network.
GAW at Empa
Mission Statement
The mission of WCC-Empa and QA/SAC Switzerland is to improve and maintain the quality and public access of surface ozone, carbon monoxide, methane and carbon dioxide data measured at Global Atmosphere Watch stations, primarily through system and performance audits at GAW stations, inter-comparison and calibration of instrumentation, one-to-one training and workshops, as well as continuous operational and strategic support for the GAW programme, in order to contribute to the scientific basis of our understanding of climate change.
From 2011 to 2016, the GAW team at Empa was also involved in the CATCOS (Capacity Building and Twinning for Climate Observing Systems) project funded by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) with MeteoSwiss as the coordinating partner. Within CATCOS, Empa was responsible for the implementation of greenhouse gas observation capabilities in Vietnam, Chile and Kyrgyzstan & associated twinning / support. To ensure sustainability of the implementation beyond the end of the project, reduced twinning & support is still provided through WCC-Empa and QA/SAC Switzerland activities.
From fall 2022 to fall 2025, some QA/SAC Switzerland activities in Africa, and in patricular in Kenya, are also supported through the KADI (Knowledge and Climate Services from an African Observation and Data Research Infrastructure) project. KADI is funded by the European Commission's Horizon Europe programme, The Swiss contribution to supported by the State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI). KADI aims at improving the knowledge about climate change in Africa, at developing tools to combat its negative consequences, and at providing concepts for developing science-based climate services in Africa. Ultimately, first steps should be taken towards a pan-African climate observation research infrastructure. QA/SAC Switzerland is mainly involved in a pilot on lessons learned from existing long-term atmospheric and ecosystem observations.
GAW Station Support


WCC-Empa (World Calibration Centre for Surface Ozone, Carbon Monoxide, Methane and Carbon Dioxide)
QA/SAC Switzerland (Quality Assurance/Scientific Activity Centre)
GAW-qc (Interactive quality control tool for atmospheric composition measurements)
GAW Report No. 312 (2025): WMO Global Atmosphere Watch (GAW) Science and Implementation Plan: 2024–2027
GAW Report No. 292 (2024): 21st WMO/IAEA Meeting on Carbon Dioxide, Other Greenhouse Gases and Related Measurement Techniques (GGMT-2022)
WMO Report No. 1215 (2021): An update on low-cost sensors for the measurement of atmospheric composition
Technical advice note on lower cost air pollution sensors (2017)
GAW Report No. 228 (2017): WMO Global Atmosphere Watch (GAW) Implementation Plan: 2016-2023
The Global Atmosphere Watch Programme: 25 Years of Global Coordinated Atmospheric Composition Observations and Analyses (2014)
-
Share