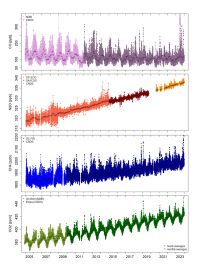
CO2, CH4, N2O, and CO greenhouse gas measurements at Jungfraujoch
The CO2, CH4, N2O and CO measurements complement the halogenated greenhouse gases measured as part of the CLIMGAS-CH (HALCLIM) / AGAGE and ICOS activities. The joint observations allow monitoring a comprehensive set of the most important greenhouse gases and make Jungfraujoch the best equipped high-altitude research station in this respect.

In late 2009, CO2 and CH4 observations were initiated with a Wavelength-Scanned Cavity Ringdown Spectrometer (CRDS) which records data in the Hz range. Due to its superior precision and the full temporal coverage, the CRDS instrument became the master instrument for CH4 observations while the GC-FID/ECD system was operated until summer 2016 to ensure a seamless transition and for quality control purposes. The CRDS model for CO2 and CH4 was replaced in September 2011 by a newer CRDS model being capable to measure CO2, CH4 and CO. Since January 2012, the data recorded with CRDS are also used as the primary CO time series.
Observations were initially coupled to an upstream installed custom-built calibration/drying unit. The sample air was dried prior to analysis by means of a Nafion dryer until August 2010. Along with CO2 and CH4, the instrument is also capable to measure water vapour. Thus, the greenhouse gas data can be corrected for interferences of remaining water traces. From August 2010 onwards, no water vapour removal was used anymore and CO2 and CH4 dry air mixing ratios were determined by application of an empirical humidity correction to the fully unaltered humid gas stream accounting for dilution and pressure broadening effects. When the CO2/CH4/H2O analyser was replaced by the four-channel (CO2/CH4/CO/H2O) analyser in September 2011, the sample air was again dried prior to analysis, mainly to improve performance of the CO observations.
In December 2014, the measurements were complemented by high-resolution, continuous N2O measurements. To do so, Empa started operating an off-axis integrated cavity output spectrometer (OA-ICOS) along with a commercially available multi-inlet unit with custom-made modifications used for calibration next to the GC-FID/ECD system. The superior precision and the continuous operation of the OA-ICOS compared to GC-ECD allow measuring short-term N2O variations that could not be detected with gas chromatography before. The laser spectrometer is also capable of measuring CO and H2O with high precision. Similar to the CRDS operation, dry air mole fractions can be determined by applying a humidity correction to the fully unaltered humid gas stream accounting for dilution and spectroscopic effects. Side-by-side N2O measurements with GC-ECD and OA-ICOS were performed until summer 2016 when the GC-ECD was dismantled. The OA-ICOS observations needed to be stopped in November 2019 due to severe instrumental issues.

-
Share