Synthesis of core-shell nanoparticles
It has been shown in the literature that conductive fillers can be used to increase the ε’ of a matrix when the concentration of the filler approaches percolation threshold. However, special care has to be taken to avoid formation of conductive paths through the material. Therefore we equip conductive fillers with an insulating shell prior blending. This is a powerful means to avoid formation of conductive paths through the blended film even when particles agglomerated. We concentrate on two fillers: silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) coated with a silica shell and polyaniline coated with polydivinylbenzene shell. Elastomers with excellent mechanical properties and increased permittivity are achieved this way.
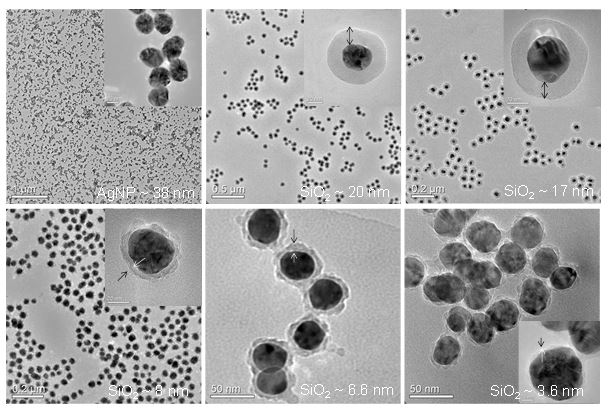
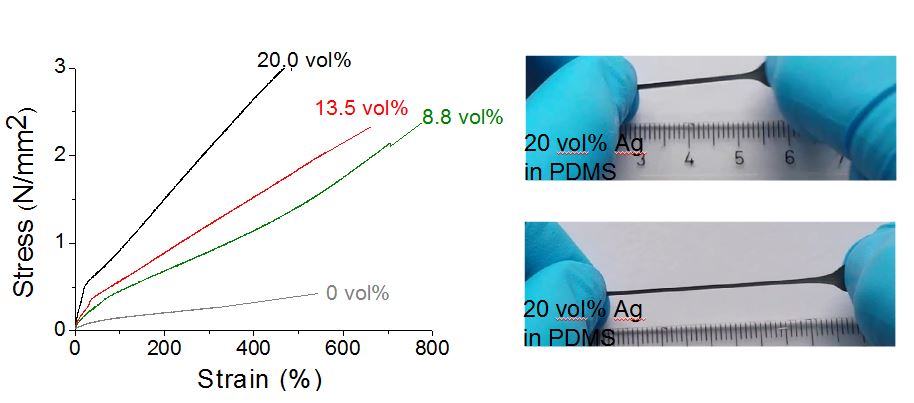
Figure: Core/shell nanoparticles having metallic AgNPs cores of ~38 nm in diameter and silica shells of different thicknesses ranging from ~ 3.6–20 nm (left), stress strain curves of AgNPs composites in silicones (middle), and photo a composite of 10 vol% of AgNPs in a polydimethylsiloxane matrix.
References:
J. E. Q. Quinsaat, et al., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 14675-14685; J. E. Q. Quinsaat, et al., RSC Advances, 2013, 3, 6964-6971; D. M. Opris, et al., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2011, 21, 3531-3539; M. Molberg, et al., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2010, 20, 3280-3291.
-
Share
