Stray Field Components
Because the MFM scans a space devoid of sources of magnetic field, in practice we can write the latter as the gradient of a magnetic potential, , where
satisfies the Laplace equation. For definiteness we assume the sources of the stray field (provided by the sample) are described by a boundary condition on the xy-plane, parallel to the scan plane located at distance z from the top surface of the sample. In the 2D Fourier space utilized in the previous section, this leads to the convenient expression
|
|
|
and therefore also to
|
|
|
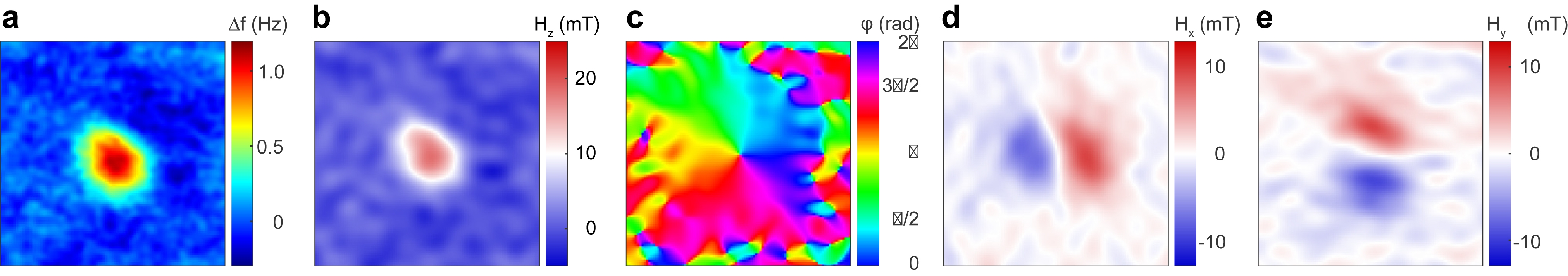
a MFM data of a skyrmion in a [Ir1/Co0.6/Pt]x6 multilayer thin film. b Hz at z = 12nm obtained from the deconvolution of a using qMFM methods. d, e Hx, and Hy components obtained from Hz, and c color wheel representation of the in-plane stray field components.
-
Share
