Modelling-based evaluation of heat prevention and protection strategies
The application of reliable models of human thermal physiology enables an efficient screening of heat exposure scenarios considering personal body condition, activity, clothing, and environmental thermal factors.
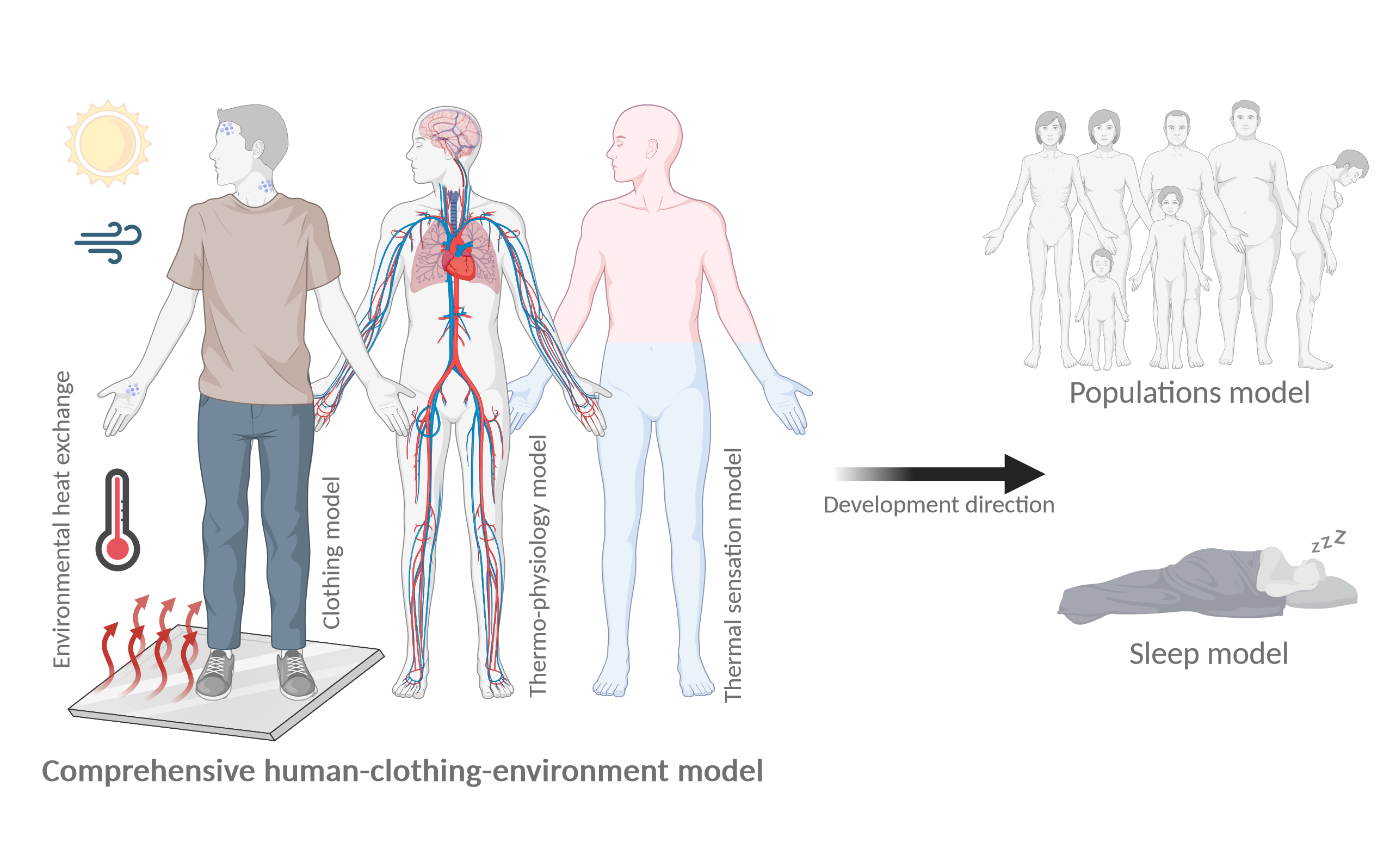
In the era of ever-increasing computational capabilities, a plethora of heat exposure scenarios combined with human characteristics can be screened quickly for factors indicating the level of heat strain and stress. The necessary basis is a sequence of reliable simulation tools, including:
- Physiological model to assess the impact of heat exposure on acute and chronic responses of the human body, able to reflect different types of populations and their heat tolerance issues (inherent body condition and behaviour).
- Clothing model to realistically represent the heat transfer barrier close to the human body with regards to radiation (solar or from hot surfaces), convection (ventilation and effect of wind), and evaporation (allowing body cooling by sweat evaporation).
As a result, the environmental and personal conditions that potentially lead to heat stress can be mapped, and mitigation measures to avoid it can be proposed and tested fully virtually. Finally, the efficacy, effectiveness and efficiency of mitigation measures can be directly estimated and compared against the effort and the costs of individual heat mitigation strategies, including estimation of productivity loss, target environmental settings and recommendations for clothing and pace.
