Nanomedicine
Gentler tumor treatment
Radiation therapy is one of the cornerstones of cancer therapy. However, some types of tumor respond little or hardly at all to radiation. If it were possible to make tumor cells more sensitive, treatment would be more effective and gentler. Empa researchers have now succeeded in using metal oxide nanoparticles as "radiosensitizers" – and in producing them on an industrial scale.

Today, various treatment methods are available for cancer that can complement each other. Radiation therapy is frequently used, and can be combined with surgery and chemotherapy, for example. Although treatment with ionizing radiation has been used in medicine for more than 100 years, even modern oncology is sometimes not satisfied with its effectiveness. The reason: Malignant tumors are not always sensitive enough to radiation. "If the sensitivity of the tumor cells could be increased, radiotherapy could be carried out more effectively and more gently," says Empa researcher Lukas Gerken.
In other words: A desired treatment outcome could be achieved with a lower dose of radiation than is currently the case, or particularly radiation-resistant tumors could finally become sensitive to radiation. The team led by Lukas Gerken and Inge Herrmann from the "Particles-Biology Interactions Laboratory" at Empa in St. Gallen and the "Nanoparticle Systems Engineering Laboratory" at ETH Zurich is therefore working with oncologists at the Cantonal Hospital in St. Gallen to find ways to sensitize tumor cells to radiation.
The researchers have set their sights on nanoparticles made of metal oxides that can act as so-called radiosensitizers. The team has now succeeded in producing these radiosensitizers in large quantities and analyzing their effect in more detail. The researchers recently published their results in the journal Chemistry of Materials.
Cured in the fire
In cancer research, studies are currently underway with various classes of substances to make the irradiation of tumors more effective. Exactly how nanoparticles made of gold or more exotic metal oxides such as hafnium dioxide work in this context is not yet fully understood. What is known, though, is that a complex reaction cascade exerts oxidative stress in cancer cells. In this way, the repair mechanisms of the malignant cells may be overwhelmed.
In order for the nanoparticles to be made available for clinical use, two hurdles had to be overcome: Production via conventional wet chemistry methods makes it difficult to produce quantities on an industrial scale, and there is a lack of comparative analyses on the efficacy of different substances.
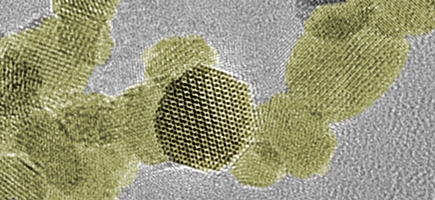
Empa researcher Gerken has now succeeded in producing metal oxide radiosensitizers using a method that is ideally suited to industrial applications: He relied on flame synthesis to obtain top-quality oxides of hafnium, zirconium and titanium. "Thanks to this production method, it is even possible – depending on the production facility – to synthesize several kilograms per day," explains Gerken. For the laboratory analyses at Empa, however, the scientist made do with just a few grams.
Shiny little helpers
 The chemical element hafnium is named after the place it was discovered, Copenhagen (Hafnia in Latin). The chemist and Nobel Prize winner George de Hevesy and the physicist Dirk Coster were finally able to detect the element from the titanium group in 1923 by means of X-ray spectroscopy, after various scientists such as Nobel Prize winner Niels Bohr had long suspected its existence. Hafnium does not normally occur in the human body and is non-toxic. In oncology, it is hoped that hafnium will have a supporting effect in the treatment of cancer. First clinical trials have already been completed.
The chemical element hafnium is named after the place it was discovered, Copenhagen (Hafnia in Latin). The chemist and Nobel Prize winner George de Hevesy and the physicist Dirk Coster were finally able to detect the element from the titanium group in 1923 by means of X-ray spectroscopy, after various scientists such as Nobel Prize winner Niels Bohr had long suspected its existence. Hafnium does not normally occur in the human body and is non-toxic. In oncology, it is hoped that hafnium will have a supporting effect in the treatment of cancer. First clinical trials have already been completed.
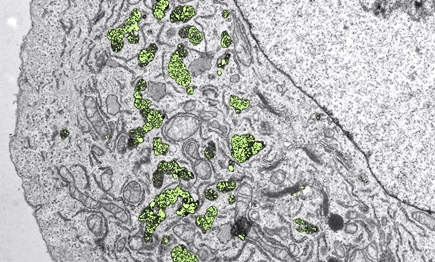
Inside the cell: Nanoparticles of hafnium dioxide (yellow-green) accumulate in cancer cells and can cause cell damage after irradiation. (Electron microscopy, colored) Image: Empa/ ETH Zurich
Better than gold
Once the nanoparticles were available in suitable quantities, Lukas Gerken was able to screen the "gems" in detail, for example using X-ray spectroscopy and electron microscopy. His verdict: "We can produce sterile, high-quality metal oxide nanoparticles that appear harmless to healthy cells," the researcher explains. He proved this using cell cultures that he treated with different nanoparticle suspensions in the lab. The metal oxides accumulated in large quantities inside the cells. The front-runner was hafnium dioxide: Here, half a billion nanoparticles entered each individual cell without being toxic. Compared to the metal oxides, nanogold did much worse with the same particle size: About 10 to 30 times fewer gold particles made it into the cell.
As harmless as the substances initially are to healthy cells, they unfold their effects powerfully when used in radiation. The team was able to demonstrate this using cancer cell lines. If the cell cultures were treated with metal oxides and then bombarded with X-rays, the killing effect increased significantly. Hafnium dioxide turned out to be the most potent tool: Tumor cells treated with hafnium particles could be eliminated with less than half the radiation dose. This first comparative study also showed that hafnium dioxide is even four times more effective than nanogold and titanium dioxide. Healthy human cells (so-called fibroblasts), on the other hand, showed no negative radiation effects after nanoparticle treatment.
The results make Lukas Gerken confident: "We will continue on this path to explore the nanoparticles' mechanism of action and further optimize their efficiency." He hopes that his studies will thus advance the clinical application of nanoparticles in radiation therapy.
| Further information Lukas Gerken | Editor / Media contact |